Concept of SDN QoS in 5G networks
Concept and QoS requirements in 5G networks
http://www.raenitt.ru/publication/T-COM_9_2014.pdf
In this article the requirements to some number of KPI that determine the quality of service in 5G networks are formulated. The proposed QoS requirements are based on the analysis of functional requirements to 5G networks and traffic parameters for HD video and massive M2M services which will the highly demanded in 2020. One of the 5G development paradigms is the virtualization of network functions (VFN) including cloud radio access network and cloud core network. The authors have proposed the concept of function blocks CQMF and CQCF to control and monitor QoS, which are implemented as part of the cloud infrastructure of 5G network.
5G network infrastructure will be based on the use of cloud technologies, both in radio access networks (Cloud RAN) with using SDR (software defined radio) infrastructure and in core network (Cloud CN) with using SDN (software defined network) infrastructure. Full virtualization of NFV network functions implemented in 5G infrastructure will take place. This virtualization of NFV network functions should cover the control and management of QoS, the service policy and prioritization of traffic.
During the evolution of QoS management mechanism in 3GPP (GSM/UMTS/LTE) networks there was a migration from QoS management at the user equipment level to the QoS management at the network level. This approach to QoS management will be maintained in 5G networks as well.The service of streaming video transfer without buffering is very sensitive to network delay, so one of the most important parameters that determine QoS requirements is the total packet delay budget (PDB).
Quality of Service Management in 5G Broadband Converged Networks
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7324643
In order to provide end-to-end QoS support for application services over the converged networks in 5G, a common QoS framework is proposed. It consists of a two-level scheduling scheme; Priority Queuing (PQ) discipline and ClassBased Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) discipline in the first level while Deficit Weighted Round Robin (DWRR) discipline is deployed in the second level. Simulation results show a seamless QoS deliverable over a vertical hand-off between LTE and a wireline network, in addition to performance improvements of Real Time (RT) applications when compared to existing scheduling systems.
SDN for 5G
Maede Zolanvari Rotation October 2015
http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse570-15/ftp/sdnfor5g.pdf
The 5G is going to be based on user-centric concept instead of operator-centric as in 3G or service-centric as seen for 4G. Hence, multiple incoming flows from different technologies would be combined at mobile stages [1].
This new generation 5G of wireless broadband network will provide the fundamental infrastructure for billions of new devices with less predictable traffic patterns will join the network. To be succeed with this new technology, going through intelligence is really crucial, to proceed to successful deployment and realization of a powerful wireless world. Principals of virtual network management and operation, which can be implemented by network function virtualization (NFV), and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) are the main element of the network architecture.
Managing and operating of the network should be based on the applications that are utilizing the network. It deals with the QoS and policies that is dictated over the network, hence it should be application driven. Application-driven networks consist of interconnecting end-user devices, different modules, and several machines, sensors, and actuators, with billions of clients connected to the Internet for supplying big data applications.
5G networks will not be based on routing and switching technologies anymore [4]. Additionally, 5G systems will be autonomous and sufficiently able to adapt the situations depending in required QoS to handle application-driven networks dynamically. Security, resiliency, robustness and data integrity will be the first priority in the design of future networks [5].
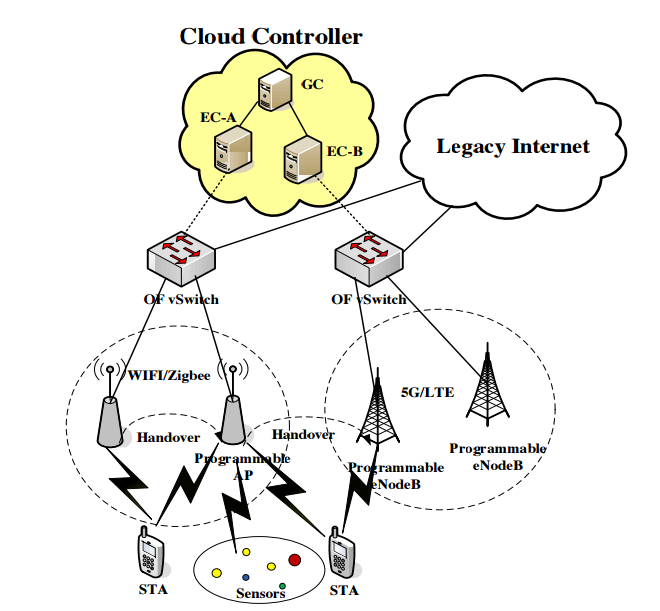
The end users’ terminals make the final choice among different access networks for the best connection. Also, the terminals will also stay awake and looking for to choose the best technology to connect, with respect to the dynamic changes at the current access technology. The infrastructure of the wireless networks will be based on SDN, which provides arrange the communication between the applications and services in the cloud and user’s mobile terminal. Therefore, the network can be managed on the real-time needs and status dynamically, and it will have benefit from resource virtualization. The architecture of 5G network based on SDN scheme has shown in Fig
The main limitation is on the computing capabilities and resources of mobile devices. As a result because mobile users send request over and over to the embedded controller for flow rules in OpenFlow messages, the overhead increases more significantly
The main idea of introducing SDN is to separate the control plane outside the switches and enable external control of data through a logical software component called controller. SDN provides simple abstractions to describe the components, the functions they provide, and the protocols to manage the forwarding plane along with Mobile IP from a remote controller via a secure channel. Hence, the controller monitors network packets, publishes policy, or solves errors according to the monitoring results.
The OpenFlow standard has been exploited as the dominant technology for the southbound interface (connection between the control plane and network devices). This scheme allows on-demand resource allocation, self-service provisioning, completely virtualized networking, and secures cloud services.

评论
发表评论